Benedict Roth spirometer measures oxygen consumption for measuring the basal metabolic rate, lung volumes, and capacities. This device could be used for measuring Vital capacity (VC), tidal volume (VT), inspiratory and expiratory reserve volumes (IRV ERV), as well as Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1).
A spirometer cannot measure Residual volume, functional residual capacity, and total lung capacities.

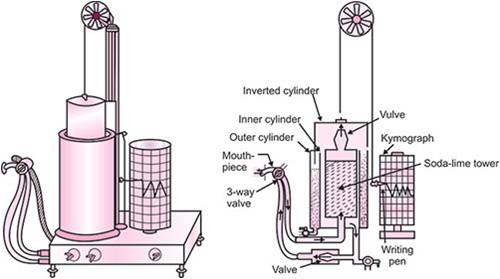
Parts of Benedit Roth spirometer are:
1. Inverted cylinder: It is also called Bell. It is a cylinder of 9 liters capacity made of lightweight metal which dips into this water from above. The top of the bell carries a hook to which a chain is attached. The chain passes over a frictionless pulley and carries a counterweight and a pen. This pen moves up and down as the Volume of air in the bell decreases or increases, thus the bell displacements are recorded on the kymograph.
2. Inner cylinder: it is composed of soda lime that is to remove the carbon dioxide from expired air. The end of the cylinder is attached to the one-way valve so that no gas can exit.
3. Soda lime tower: It is fitted within the spirometer and removes carbon dioxide from the expired air so that one can breathe in and out through the mouthpiece.
2. Outer cylinder: A double-walled cylindrical chamber containing water is formed with the help of an outer cylinder that maintains an airtight seal.
3. Breathing assembly, i.e. breathing valves with mouthpiece: There are two unidirectional breathing valves, one for inspiration and the other for expiration. These are connected with the help of a Y-shaped piece to a free-breathing valve. The free-breathing valve is a bore metallic tube having a bi-directional tap that can be turned to allow the subject either to breathe room air or spirometric air
4. Pulley: Inverted cylinder is hooked with the chain that passes through the pulley and is attached to the writing pen that will make a change in volumes in the kymograph.
5. Writing pen: Traditional instruments will have a writing pen that should be filled with ink.
7. Tap: for the drainage of the water
8. Gas inlet: There is a slot for the Gas inlet usually oxygen is passed through that inlet
6. Kymograph: Graph paper is attached in this segment. There is an on/off switch and speed regulator that will revolve the kymograph with the different speed marks in the instrument. Change in other volumes is air is plotted in the graph paper.
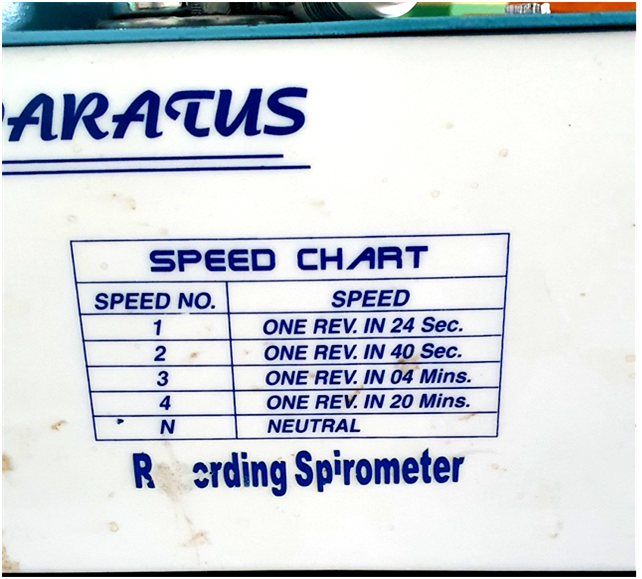
7. Graph paper: it varies according to the model of the Benedict Roth spirometer.

Chart paper: calibration
Y-Axis represents volume and 1 row represents 100ml
X-axis represents time.
For eg at a drum speed of one revolution in 24 sec, it will take 2 sec to cover 1 column
How does Benedict Roth’s spirometer work?
Principle: The bell is dipped into the water for an airtight seal and oxygen gas is inserted from the gas outlet. The bell began to rise and stop inserting the gas till 1/3 portion of the bell remain in the water. The top of the bell carries a hook to which a chain is attached. The chain passes over a frictionless pulley and carries a counterweight and a pen. During inspiration, the bell moves down and the pen moves upward whereas during expiration the bell moves upward and the pen moves down. This pen moves up and down as the Volume of air in the bell decreases or increases, thus the bell displacements are recorded on the kymograph.